|
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- Wi.232 Moduls
- Download Configuration Tool
- Adapter Board
- Layout / wiring diagram
- Placement
- BOM (Bill of Material)
- Assembly
- Ribbon cable
- Start up
- Configuration
- TIP!
- Note:
- Connection to SerCon / MK-USB
- Connection to FC
- Connection to NC
- Rangeextender for PC or Cell (DubWise)
- Range Test
- Yagi-antenna for greater distance
- Problems
Wi.232 Moduls
Shoplink Wi.232 Funkmodul+Adapterplatine
Shoplink Wi.232 Funkmodul
The Wi.232 modules of Radiotronix are a family of wireless modems for wireless bridging and designed especially for serial UARTs. Inside of this family there are several pin-compatible module versions:
Modul description |
Frequency range |
Transmitting Power |
Modulation |
Description |
Wi.232DTS-R |
902 - 928 MHz |
25 mW |
FSK/DTS |
Embedded Radio Module with MCU, Transparent UART to RF Digital Transmission System (DTS) SW protocol (North America) |
Wi.232FHSS-25-R |
902 - 928 MHz |
25 mW |
FHSS/FSK |
Embedded Radio Module with MCU, 25mW, Transparent UART to RF Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS) Protocol (North America) |
Wi.232DTSB-R |
902 - 907.5 & 915 - 928 MHz |
25 mW |
FSK/DTS |
Embedded Radio Module with MCU, Transparent UART to RF Digital Transmission System (DTS) SW protocol, Anatel Certified (Brazil) |
Wi.232EUR-R |
868 - 870 MHz |
32 mW |
FSK/DTS |
Embedded Radio Module with MCU, Transparent UART to RF Digital Transmission System (DTS) SW protocol, ETSI Regulations Compliant (Europe) |
All modules require a power supply of 2.7 - 3.6 volts at a current of max. 65 mA and support baud rates from 2400 up to 115,200. On this Paparazzi page you will be discouraged from using the North America version, since they may interfere with GPS reception.
The modules you can get here:MK-Shop
Download Configuration Tool
Adapter Board
![]() The adapter board is suitable for the MikroKopter as well as for the PC side! On the PC side the module is connected to the MK-USB. To use these modules in addition to a suitable antenna (a 8.6 cm long isolated wire) you may need an adapter board, which handles the voltage supply and the level shifter from 5V TTL to 3.3V or 3V TTL. The adapter board was developed following the recommendation of the Modul-Datenblattes and the Bluetooth Adapter BT-AP10.
The adapter board is suitable for the MikroKopter as well as for the PC side! On the PC side the module is connected to the MK-USB. To use these modules in addition to a suitable antenna (a 8.6 cm long isolated wire) you may need an adapter board, which handles the voltage supply and the level shifter from 5V TTL to 3.3V or 3V TTL. The adapter board was developed following the recommendation of the Modul-Datenblattes and the Bluetooth Adapter BT-AP10.
There are two versions of the adapter board which differ only slightly.
Old Version
Version V1.3

Layout / wiring diagram
Old Version
Version V1.3
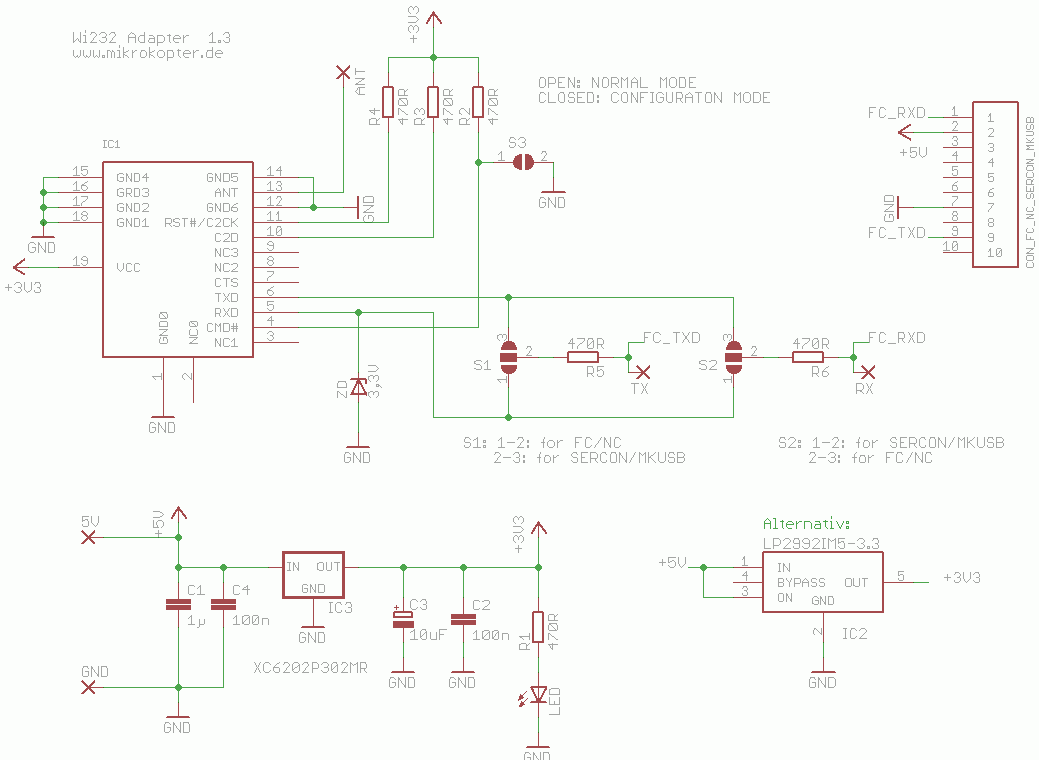
Placement
Old Version
Version V1.3
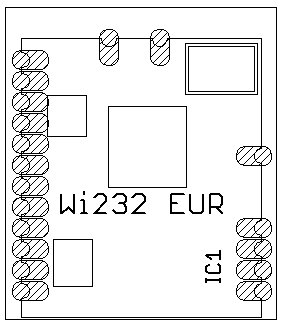
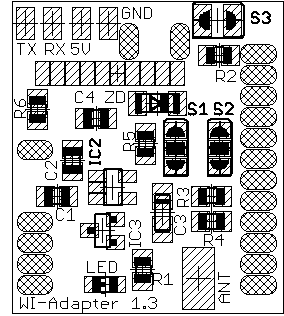
BOM (Bill of Material)
Old Version |
Name |
Number |
Description |
Ordering Number |
Note |
IC1 |
1 |
WI.232EUR-R |
MK-Shop or Sander Electronics |
All Versions |
IC2 |
1 |
LP2992IM5-3.3 |
CSD Elektronics 22-2992V03,3 |
Voltage Converter 3,3V |
C1 |
1 |
0805 KerKo 1 µF / 16V |
CSD Elektronics 115-08R001 |
|
C2 |
1 |
0805 KerKo 100 nF |
CSD Elektronics 115-08N100 |
|
C3 |
1 |
T4.7µF / 10V |
CSD Elektronics 121-A10R004,7 |
Watch Polarity !! |
R1 |
1 |
0805 SMD 330 Ohm |
CSD Elektronics 10-080330 |
|
R2, R3, R4, R5, R6 |
5 |
0805 SMD 1k Ohm |
CSD Elektronics 10-08K001 |
|
LED |
1 |
LED 0805 GRN |
CSD Elektronics 26-0802017 |
All Versions, Watch Polarity |
ZD |
1 |
Z-Diode SMD 3,3V |
CSD Elektronics 13203 |
All Versions, Watch Polarity ! |
S3 |
1 |
Pin-header 2-pole RM 2.54 mm |
CSD Elektronics 01541 |
All Versions, only for programming the modules |
Ribbon cable |
1 |
10 Pol, RM 1.27mm |
CSD Elektronics 456-10 |
Pin 1 (red wire shows to R6) |
Header Connector |
1 |
10 Pole, IDC socket |
CSD Elektronics 015-PF10 |
|
Antenna |
1 |
8.6 cm wire stub |
- |
Lamda/4 of 870MHz |
V1.3 |
Name |
Number |
Description |
Ordering Number |
Note |
IC1 |
1 |
WI.232EUR-R |
MK-Shop or Sander Electronics |
All Versions |
IC3 |
1 |
XC6202P302MR |
??? |
alternativ to IC2 (3V) |
C1 |
1 |
0805 KerKo 1 µF / 16V |
CSD Elektronics 115-08R001 |
|
C2, C4 |
2 |
0805 KerKo 100 nF |
CSD Elektronics 115-08N100 |
|
C3 |
1 |
T10 µF / 10V |
121-A10R010 |
Watch Polarity (Currently one KerKo is supplied by the MK-Shop, here you don't have to watch the polarity!) |
R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6 |
6 |
0805 SMD 470 Ohm |
CSD Elektronics 10-080470 |
|
LED |
1 |
LED 0805 GRN |
CSD Elektronics 26-0802017 |
All Versions, Watch Polarity! |
ZD |
1 |
Z-Diode SMD 3,3V |
CSD Elektronics 13203 |
All Versions, Watch Polarity! |
S3 |
1 |
Pin header 2-pole RM 2.54 mm |
CSD Elektronics 01541 |
All Versions, only for the programming of the modules |
Ribbon cable |
1 |
10 ole, RM 1.27mm |
CSD Elektronics 456-10 |
Pin 1 (red wire points to R6) |
Header Connector |
1 |
10 pole, IDC socket |
CSD Elektronics 015-PF10 |
|
Antenna |
1 |
8.6 cm wire stub |
- |
Lamda/4 of 870MHz |
In the MK-Shop you can get a set with all components.
Assembly
First you need to solder the resistors R1 to R6, the IC3 (IC2 remains unpopulated here), the diodes D1, D2 and capacitors C1 to C4 at the bottom of the board.
Then you need to assemble the jumper S3 and possibly the 10-pin ribbon cable with Pin1 (red side) down to R6.
Now you check for shorts and put 5V on a trial basis between the 5V and GND pad.
The green LED should light and between the GND pad and the pad of the separately module located between R6 and C1 there should be 3.3V or 3V (at XC6202P302MR) applied.
![]() Attention! Only after the test was successful you solder the Wi.232 module on the other side of the board and check the pads of the module for short circuits (very narrow pitch, threat of destruction of the Wi.232 module!). Only the four-row should have a short circuit between all four pins, otherwise not be measured between adjacent pins.
Attention! Only after the test was successful you solder the Wi.232 module on the other side of the board and check the pads of the module for short circuits (very narrow pitch, threat of destruction of the Wi.232 module!). Only the four-row should have a short circuit between all four pins, otherwise not be measured between adjacent pins.
At the end the wire stub can be added to the pad of the antenna.
The result looks like this:
![]() In the old layout unfortunately an error crept in so that GND is tapped at pin 7 of the 10-pin ribbon cable to the board at pin 8. This explains the small patch in the upper right picture. On the ribbon cable pin 8 is "unproductive" and bridged on the PCB with pin 7 & 8
In the old layout unfortunately an error crept in so that GND is tapped at pin 7 of the 10-pin ribbon cable to the board at pin 8. This explains the small patch in the upper right picture. On the ribbon cable pin 8 is "unproductive" and bridged on the PCB with pin 7 & 8
Is resolved in V1.3 !
Ribbon cable
The ribbon cable should be about 9cm long. The transmitter then has some distance to the remaining electronic. In addition the ribbon cable is then the opposite pole of the antenna.
![]() Because the modules are sensitive to electrostatic they should be used only shrunk. In addition avoid the direct touch of the antenna!
Because the modules are sensitive to electrostatic they should be used only shrunk. In addition avoid the direct touch of the antenna!
Start up
To configure the module you need first a serial connection with 5V-level to a Windows PC.
The easiest way is it to use the MK-USB. Alternatively you can also use the SerCon (connected to SIO). The 5V supply must be extra created when using the SerCon.
Using the SerCon it must be necessarely be connected for communication with the CTS and RTS-Line of the Sub-D-socket of the Sercon. This is necessary so the level of the CTS line is high. Only in this way a connection with the tool Radiotronix can be set up (Sub-D-socket, connect Pin 7 and 8 at the Standard 9pol. RS 232). You can also have a small toggle switch directly soldered to the pins, and so those have on-demand connection.
To connect the PC to the copter two identical Wi232 modules are required.
To program the modules the jumpers S1 and S2 for TxD / RxD have to be soldered as follows:
Jumper for programming
![]() N O T E: the Wi232 module on the PC (connected via the USB MK) and the module on the Kopter are jumpered differently after programming for TxD / RxD over the jumper S1/S2:
N O T E: the Wi232 module on the PC (connected via the USB MK) and the module on the Kopter are jumpered differently after programming for TxD / RxD over the jumper S1/S2:
Jumpers for connecting the Wi232 to the PC (via USB MK).
Jumpers for connecting the Wi232 to the Kopter.
Configuration
Now install the Setup Tool: Download .
Before the program starts the Wi232 should be set into programming mode. For this purpose, S3 is bridged at Wi232. On MK-USB attach the jumper for the 5V supply. Now plug the Wi232 to the MK-USB. The software can be started. Here is the correct interface selected and sets the baud rate to 2400.
The settings are set as shown in the red circles
![]() "Network Mode Register" at the Wi.232 for MK to "Slave", and for the PC Side to "Normal".
"Network Mode Register" at the Wi.232 for MK to "Slave", and for the PC Side to "Normal".
The values can be stored in each set with the "Write" button.
After all values have been stored, the jumper can be removed on Wi232. After that the program can be closed.
Click on the picture you can see in addition (bottom center), the three status indicators for TXD,RXD and CTS. It can be seen very well if for the use of the SerCon the CTS and RTS-Lines are connected so that can be established a connection (bride green glow of the CTS-status display). For safety, you can as shown above press the read button to verify the setting (for more details see Datenblatt.pdf ).
After writing the values you should necessarily remove the jumper from S3, otherwise the next time PowerUp resets all registers to their default settings.
Quick Guide: Program Settings:
- Place Jumper on MK-USB and Wi.232
- Connect Wi.232 to the MK-USB
- Connect MK-USB to the PC
- Start Radiotronix Software (Baud rate to 2400) and program modul
- Remove Jumper from Wi.232
- Close Radiotronix Soft
- Disconnect MK-USB from PC
- Disconnect Wi.232 from MK-USB
Quick Guide: Get Settings (to check):
- Place Jumper on MK-USB
- Connect Wi.232 to the MK-USB
- Connect MK-USB to the PC
Now place the jumper on the Wi.232 !
- Start Radiotronix Software (Baud rate now to 57600!)
- Check settings of the modul
- Remove jumper from Wi.232
- Close Radiotronix Software
- Disconnect MK-USB from PC
- Disconnect Wi.232 from MK-USB
The important point is: Place the jumper of the Wi.232 after power is supplied! So the modul is turning into the Command-Mode. The parameters are not deleted.
(tbd. Register für MTU & Tx-Timeout auf serielles Protokoll / FW-Update optimieren)
TIP!
Are the jumper for Tx and Rx already set for connection of the MK and the MK-USB and the module is shrunk so it is no longer possible for the MK to operate the MK-USB module, for example to re-program it.
The solution: You should solder a 10 pin male connector / socket connector - adapter where the Tx and Rx line been crossed, ground and +5 V can be looped through one to one.
Thus you can connect the module back from the MK to the MK-USB without removing the heat shrink stubing and without soldering the Tx / Rx jumpers back.
Note:
- There is a slight difference in setting up the module for the MK and the one for the USB link. The one connected to the USB link will have to be set up as "Normal" under the "Network Mode Register" and the one connected to the MK will have to be set to "Slave" for the Wi.232 link to work properly.
Connection to SerCon / MK-USB
see above, Note to 5V Supply
Connection to FC
Pin 1 is marked with the red arrow. The power supply of the Wi232 via the FC.
Connection to NC
Pin 1 is marked with a red arrow. The power supply of the Wi232 via the Navi.
When connected to the NC (open 10-pin debug port, pin header) all connected modules can be seen in the Koptertool (FC, NC, MK3Mag, GPS)
![]() The SW update of the NC with the WI232 modul is extremely problematic, because the upload process usually ends with an error. Obviously the serial protocol is compatible but the timing of the boot loader does not match the WI232. Therefore you should always hook up directly a cable to the NC for a software update. The software update of the MK3Mag and the FC is, however, unproblematical. Anhören Umschrift Übersetzung bewerten
The SW update of the NC with the WI232 modul is extremely problematic, because the upload process usually ends with an error. Obviously the serial protocol is compatible but the timing of the boot loader does not match the WI232. Therefore you should always hook up directly a cable to the NC for a software update. The software update of the MK3Mag and the FC is, however, unproblematical. Anhören Umschrift Übersetzung bewerten
Rangeextender for PC or Cell (DubWise)
(here in example with a Yagi-Antenna)
To implement Bluetooth on Wi232 there must be just another female connector crimped onto the cable, where the Bluetoothmodul is connected (slave mode). Both modules just only need to be supplied with voltage (4.5-12V) (plus and minus to Pin 2 to Pin 7 of the ribbon cable)
Range Test
A range test was 1300m on the ground in the line of sight, with the EUR-R Modul and 8.6 cm wire antenna. 6km with a Yagi-Antenna.
Yagi-antenna for greater distance
A UHF television antenna e.g. the UHF43of Reichelt, increases the range.
We have already received position datas from the MikroKopter 6km away.
The antenna can be shortened by the front element if that is not mounted (as in pictures). This will reduce the range somewhat, but the antenna is easier to handle and the straightening effect is not as high.
Therefore the Wi232 with adapter can be built in directly into the terminal box of the antenna. The antenna connector is soldered to the middle pin. The BNC-Connector is soldered off.
Problems
There are probably problems with the radiation to the gyros. It must be still investigated. http://forum.mikrokopter.de/topic-post113611.html
RadioTronix/../ucwiki/KategorieHardware

 Seite in
Seite in