|
Größe: 20288
Kommentar:
|
← Revision 24 vom 19.10.2024 09:30 ⇥
Größe: 20140
Kommentar:
|
| Gelöschter Text ist auf diese Art markiert. | Hinzugefügter Text ist auf diese Art markiert. |
| Zeile 7: | Zeile 7: |
| = Wi.232 Module = | = Wi.232 Moduls = |
| Zeile 25: | Zeile 25: |
| All modules require a power supply of 2.7 - 3.6 volts at a current of max. 65 mA and support baud rates from 2400 up to 115,200. On this [[http://paparazzi.enac.fr/wiki/Modems|Paparazzi]] page will be discouraged from using the North America version, since they may interfere with GPS reception. Die Module können hier:[[https://www.mikrocontroller.com/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=86&products_id=377|MK-Shop]] bezogen werden. <<BR>> = Download Konfigurationstool = <<InfoBox('''Download: http://www.mikrokopter.de/ucwiki/RadioTronix?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=WI232_setup.exe''')>> = Adapterplatine = /!\ '''Die Adapterplatine ist sowohl für den MK, als auch für die PC-Seite geeignet! Auf der PC-Seite wird das Modul an den MK-USB angeschlossen.''' Um diese Module verwenden zu können, benötigt man neben einer passenden Antenne (eine 8,6cm langer '''isolierter''' Draht) noch eine Adapterplatine, welche die Spannungsversorung und den Levelshifter von 5V TTL auf 3.3V bzw.3V TTL erledigt. Die Adapterplatine entstand in Anlehnung an die Empfehlung des [[http://www.radiotronix.com/datasheets/new/eur_um.pdf|Modul-Datenblattes]] und des Bluetooth Adapters [[BT-AP10]].<<BR>> <<BR>> Es gibt zwei Versionen der Adapterplatine, die sich nur gering unterscheiden. == alte Version == {{attachment:WI232_Board_Plain.JPG}} |
All modules require a power supply of 2.7 - 3.6 volts at a current of max. 65 mA and support baud rates from 2400 up to 115,200. On this [[http://paparazzi.enac.fr/wiki/Modems|Paparazzi]] page you will be discouraged from using the North America version, since they may interfere with GPS reception. The modules you can get here:[[https://www.mikrocontroller.com/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=86&products_id=377|MK-Shop]] <<BR>> = Download Configuration Tool = <<InfoBox('''Download: http://wiki.mikrokopter.de/RadioTronix?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=WI232_setup.exe''')>> = Adapter Board = /!\ '''The adapter board is suitable for the MikroKopter as well as for the PC side! On the PC side the module is connected to the MK-USB.''' To use these modules in addition to a suitable antenna (a 8.6 cm long '''isolated''' wire) you may need an adapter board, which handles the voltage supply and the level shifter from 5V TTL to 3.3V or 3V TTL. The adapter board was developed following the recommendation of the [[http://www.radiotronix.com/datasheets/new/eur_um.pdf|Modul-Datenblattes]] and the Bluetooth Adapter [[BT-AP10]].<<BR>> <<BR>> There are two versions of the adapter board which differ only slightly. == Old Version == {{http://mikrokopter.de/ucwiki/RadioTronix?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=WI232_Board_Plain.JPG}} |
| Zeile 41: | Zeile 41: |
| {{attachment:Wi232-V1_3-1.jpg}} | {{http://mikrokopter.de/ucwiki/RadioTronix?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=Wi232-V1_3-1.jpg}} |
| Zeile 47: | Zeile 47: |
| = Schaltplan = == alte Version == {{attachment:WI232_Board_Sch.JPG}} |
= Layout / wiring diagram = == Old Version == {{http://mikrokopter.de/ucwiki/RadioTronix?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=WI232_Board_Sch.JPG}} |
| Zeile 52: | Zeile 52: |
| {{attachment:Wi232_1_3_sch.gif}} = Bestückungsplan = == alte Version == {{attachment:WI232_Board_Best.JPG}} |
{{http://mikrokopter.de/ucwiki/RadioTronix?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=Wi232_1_3_sch.gif}} = Placement = == Old Version == {{http://mikrokopter.de/ucwiki/RadioTronix?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=WI232_Board_Best.JPG}} |
| Zeile 59: | Zeile 59: |
| {{attachment:Wi232_1_3_Top.jpg.gif}} {{attachment:Wi232_1_3_Bot.jpg.gif}} = Stückliste = ||alte Version || |
{{http://mikrokopter.de/ucwiki/RadioTronix?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=Wi232_1_3_Top.jpg.gif}} {{http://mikrokopter.de/ucwiki/RadioTronix?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=Wi232_1_3_Bot.jpg.gif}} = BOM (Bill of Material) = ||Old Version || |
| Zeile 66: | Zeile 66: |
| ||<tablewidth="80%">'''''Name''' '' ||'''''Anzahl''' '' ||'''''Beschreibung''' '' ||'''''Bestellnummer''' '' ||'''''Hinweis''''' || ||IC1 ||1 ||WI.232EUR-R ||[[https://www.mikrocontroller.com/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=86&products_id=377|MK-Shop]] oder Sander Electronics ||alle Versionen || ||IC2 ||1 ||LP2992IM5-3.3 ||CSD Elektronics 22-2992V03,3 ||Spannungswandler 3,3V || |
||<tablewidth="80%">'''''Name''' '' ||'''''Number''' '' ||'''''Description''' '' ||'''''Ordering Number''' '' ||'''''Note''''' || ||IC1 ||1 ||WI.232EUR-R ||[[https://www.mikrocontroller.com/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=86&products_id=377|MK-Shop]] or Sander Electronics ||All Versions || ||IC2 ||1 ||LP2992IM5-3.3 ||CSD Elektronics 22-2992V03,3 ||Voltage Converter 3,3V || |
| Zeile 71: | Zeile 71: |
| ||C3 ||1 ||T4.7µF / 10V ||CSD Elektronics 121-!A10R004,7 ||Polung beachten || | ||C3 ||1 ||T4.7µF / 10V ||CSD Elektronics 121-!A10R004,7 ||Watch Polarity !! || |
| Zeile 74: | Zeile 74: |
| ||LED ||1 ||LED 0805 GRN ||CSD Elektronics 26-0802017 ||alle Versionen, Polung beachten || ||ZD ||1 ||Z-Diode SMD 3,3V ||CSD Elektronics 13203 ||alle Versionen, Polung beachten || ||S3 ||1 ||Stiftleiste 2-Pol RM 2.54 mm ||CSD Elektronics 01541 ||alle Versionen, dient zur Programmierung des Moduls || ||Flachbandkabel ||1 ||10 Pol, RM 1.27mm ||CSD Elektronics 456-10 ||Pin 1 (rote Ader zeigt zu R6) || ||Pfostensteckverbinder ||1 ||10 Pol, Schneidklemm-Buchse ||CSD Elektronics 015-PF10 || || ||Antenne ||1 ||8.6 cm Drahtstummel ||- ||Lamda/4 von 870MHz || |
||LED ||1 ||LED 0805 GRN ||CSD Elektronics 26-0802017 ||All Versions, Watch Polarity || ||ZD ||1 ||Z-Diode SMD 3,3V ||CSD Elektronics 13203 ||All Versions, Watch Polarity ! || ||S3 ||1 ||Pin-header 2-pole RM 2.54 mm ||CSD Elektronics 01541 ||All Versions, only for programming the modules || ||Ribbon cable ||1 ||10 Pol, RM 1.27mm ||CSD Elektronics 456-10 ||Pin 1 (red wire shows to R6) || ||Header Connector ||1 ||10 Pole, IDC socket ||CSD Elektronics 015-PF10 || || ||Antenna ||1 ||8.6 cm wire stub ||- ||Lamda/4 of 870MHz || |
| Zeile 91: | Zeile 91: |
| ||<tablewidth="80%">'''''Name''' '' ||'''''Anzahl''' '' ||'''''Beschreibung''' '' ||'''''Bestellnummer''' '' ||'''''Hinweis''''' || ||<#ffff00>IC1 ||<#ffff00>1 ||<#ffff00>WI.232EUR-R ||<#ffff00>[[https://www.mikrocontroller.com/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=86&products_id=377|MK-Shop]] oder Sander Electronics ||<#ffff00>alle Versionen || ||<#ffff00>IC3 ||<#ffff00>1 ||<#ffff00>XC6202P302MR ||<#ffff00>??? ||<#ffff00>alternativ zu IC2 (3V) || |
||<tablewidth="80%">'''''Name''' '' ||'''''Number''' '' ||'''''Description''' '' ||'''''Ordering Number''' '' ||'''''Note''''' || ||<#ffff00>IC1 ||<#ffff00>1 ||<#ffff00>WI.232EUR-R ||<#ffff00>[[https://www.mikrocontroller.com/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=86&products_id=377|MK-Shop]] or Sander Electronics ||<#ffff00>All Versions || ||<#ffff00>IC3 ||<#ffff00>1 ||<#ffff00>XC6202P302MR ||<#ffff00>??? ||<#ffff00>alternativ to IC2 (3V) || |
| Zeile 96: | Zeile 96: |
| ||<#ffff00>C3 ||<#ffff00>1 ||<#ffff00>T10 µF / 10V ||<#ffff00>121-A10R010 ||<#ffff00>Polung beachten (Aktuell wird ein KerKo im Set vom MK-Shop mitgeliefert, hier ist '''keine''' Polung zu beachten!) || | ||<#ffff00>C3 ||<#ffff00>1 ||<#ffff00>T10 µF / 10V ||<#ffff00>121-A10R010 ||<#ffff00>Watch Polarity (Currently one KerKo is supplied by the MK-Shop, here you '''don't''' have to watch the polarity!) || |
| Zeile 98: | Zeile 98: |
| ||<#ffff00>LED ||<#ffff00>1 ||<#ffff00>LED 0805 GRN ||<#ffff00>CSD Elektronics 26-0802017 ||<#ffff00>alle Versionen, Polung beachten || ||<#ffff00>ZD ||<#ffff00>1 ||<#ffff00>Z-Diode SMD 3,3V ||<#ffff00>CSD Elektronics 13203 ||<#ffff00>alle Versionen, Polung beachten || ||<#ffff00>S3 ||<#ffff00>1 ||<#ffff00>Stiftleiste 2-Pol RM 2.54 mm ||<#ffff00>CSD Elektronics 01541 ||<#ffff00>alle Versionen, dient zur Programmierung des Moduls || ||<#ffff00>Flachbandkabel ||<#ffff00>1 ||<#ffff00>10 Pol, RM 1.27mm ||<#ffff00>CSD Elektronics 456-10 ||<#ffff00>Pin 1 (rote Ader zeigt zu R6) || ||<#ffff00>Pfostensteckverbinder ||<#ffff00>1 ||<#ffff00>10 Pol, Schneidklemm-Buchse ||<#ffff00>CSD Elektronics 015-PF10 ||<#ffff00> || ||<#ffff00>Antenne ||<#ffff00>1 ||<#ffff00>8.6 cm Drahtstummel ||<#ffff00>- ||<#ffff00>Lamda/4 von 870MHz || Im [[https://www.mikrocontroller.com/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=86&products_id=378|MK-Shop]] gibt es auch ein Set mit allen Bauteilen. = Bestückung = Man lötet zunächst die Widerstände R1 bis R6, den IC3 (IC2 bleibt hier unbestückt), die Dioden D1, D2 sowie die Kondensatoren C1 bis C4 auf die Unterseite der Platine.<<BR>> Dann bestückt man den Jumper S3 und ggf. das 10-polige Flachbandkabel mit Pin1 (rote Seite) zu R6 hin.<<BR>><<BR>> Nun überprüft man auf Kurzschlüsse und legt testweise 5V zwischen dem 5V Pad und GND an.<<BR>> Die grüne LED sollte leuchten und zwischen dem GND-Pad und dem einzeln liegenden Pad des Moduls zwischen R6 und C1 sollten 3.3V bzw. 3V (beim XC6202P302MR) anliegen.<<BR>><<BR>> /!\ Achtung! Erst nachdem dieser Test erfolgreich war, lötet man das Wi.232-Modul auf die andere Seite der Platine und überprüft die Pads des Moduls auf Kurzschlüsse (sehr enges Rastermaß, Gefahr der Zerstörung des Wi.232-Moduls!). Nur die Vierer-Reihe sollte Kurzschlüsse zw. allen 4 Pins haben, ansonsten dürften keine zu messen sein zw. benachbarten Pins.<<BR>><<BR>> Am Ende kann der Drahtstummel am Pad für die Antenne angeschlossen werden.<<BR>><<BR>> Das Resultat sieht dann so aus: {{attachment:WI232_Board_Ready.JPG}} /!\ Im alten Layout hat sich leider noch ein Fehler eingeschlichen, so dass GND an Pin 7 des 10-pol. Flachbandkabels auf der Platine an Pin 8 abgegriffen wird. Das erklärt den kleinen Patch im oberen rechten Bild. Am Flachbandkabel wird Pin 8 "totgelegt" und auf der Platine Pin 7 u. 8 gebrückt. '''Ist in der V1.3 behoben !''' |
||<#ffff00>LED ||<#ffff00>1 ||<#ffff00>LED 0805 GRN ||<#ffff00>CSD Elektronics 26-0802017 ||<#ffff00>All Versions, Watch Polarity! || ||<#ffff00>ZD ||<#ffff00>1 ||<#ffff00>Z-Diode SMD 3,3V ||<#ffff00>CSD Elektronics 13203 ||<#ffff00>All Versions, Watch Polarity! || ||<#ffff00>S3 ||<#ffff00>1 ||<#ffff00>Pin header 2-pole RM 2.54 mm ||<#ffff00>CSD Elektronics 01541 ||<#ffff00>All Versions, only for the programming of the modules || ||<#ffff00>Ribbon cable ||<#ffff00>1 ||<#ffff00>10 ole, RM 1.27mm ||<#ffff00>CSD Elektronics 456-10 ||<#ffff00>Pin 1 (red wire points to R6) || ||<#ffff00>Header Connector ||<#ffff00>1 ||<#ffff00>10 pole, IDC socket ||<#ffff00>CSD Elektronics 015-PF10 ||<#ffff00> || ||<#ffff00>Antenna ||<#ffff00>1 ||<#ffff00>8.6 cm wire stub ||<#ffff00>- ||<#ffff00>Lamda/4 of 870MHz || In the [[https://www.mikrocontroller.com/index.php?main_page=product_info&cPath=86&products_id=378|MK-Shop]] you can get a set with all components. = Assembly = First you need to solder the resistors R1 to R6, the IC3 (IC2 remains unpopulated here), the diodes D1, D2 and capacitors C1 to C4 at the bottom of the board.<<BR>> Then you need to assemble the jumper S3 and possibly the 10-pin ribbon cable with Pin1 (red side) down to R6.<<BR>><<BR>> Now you check for shorts and put 5V on a trial basis between the 5V and GND pad.<<BR>> The green LED should light and between the GND pad and the pad of the separately module located between R6 and C1 there should be 3.3V or 3V (at XC6202P302MR) applied.<<BR>><<BR>> /!\ Attention! Only after the test was successful you solder the Wi.232 module on the other side of the board and check the pads of the module for short circuits (very narrow pitch, threat of destruction of the Wi.232 module!). Only the four-row should have a short circuit between all four pins, otherwise not be measured between adjacent pins.<<BR>><<BR>> At the end the wire stub can be added to the pad of the antenna.<<BR>><<BR>> The result looks like this: {{http://mikrokopter.de/ucwiki/RadioTronix?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=WI232_Board_Ready.JPG}} /!\ In the old layout unfortunately an error crept in so that GND is tapped at pin 7 of the 10-pin ribbon cable to the board at pin 8. This explains the small patch in the upper right picture. On the ribbon cable pin 8 is "unproductive" and bridged on the PCB with pin 7 & 8 '''Is resolved in V1.3 !''' |
| Zeile 127: | Zeile 127: |
| = Flachbandkabel = Das Flachbandkabel sollte ca. 9cm lang sein. Das Sendemodul hat dann etwas Abstand zur restlichen Elektronik. Ausserdem bildet das Flachbandkabel dann den Gegenpol der Antenne. |
= Ribbon cable = The ribbon cable should be about 9cm long. The transmitter then has some distance to the remaining electronic. In addition the ribbon cable is then the opposite pole of the antenna. |
| Zeile 136: | Zeile 136: |
| /!\ Da die Module elektrostatisch empfindlich sind, sollten sie nur eingeschrumpft verwendet werden. Ausserdem ist das direkte Berühren der Antenne zu vermeiden ! = Inbetriebnahme = Um das Modul zu konfigurieren, benötigt man zunächst eine serielle Verbindung mit 5V-Pegel zu einem Windows-PC. Am einfachsten geht es mit dem MK-USB. Alternativ kann auch das SerCon (Anschluss an SIO) verwendet werden. Die 5V Versorgung muss bei Verwendung des SerCon extra anlegen werden.<<BR>> Bei Verwendung des SerCon muss '''unbedingt''' zur Kommunikation mit den Modulen die CTS und RTS-Leitung der Sub-D-Buchse am SerCon verbunden werden. Dies ist notwendig damit der Pegel der CTS-Leitung auf High geht. Nur so kann mit dem Radiotronix-Tool überhaupt eine Verbindung aufgebaut werden (Sub-D-Buchse, Pin 7 und 8 verbinden, an der Standard 9pol. RS 232 Belegung ). Man kann sich auch einen kleinen Kippschalter direkt an den Pins anlöten und so bei Bedarf diese Verbindung herstellen.<<BR>><<BR>> Zur Verbindung des PC mit dem Kopter werden zwei identische Wi232 Module benötigt.<<BR>> Zum Programmieren der Module müssen die Lötjumper S1 und S2 für TxD/RxD wie folgt gelötet werden:<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:WI232-Jumper-1.JPG}} Lötjumper zum Programmieren <<BR>><<BR>> /!\ '''Zur Beachtung''': Das Wi232 Modul am PC (angeschlossen über das MK-USB) und das Modul am Kopter werden '''nach''' der Programmierung unterschiedlich für TxD/RxD über die Lötjumper S1/S2 gejumpert:<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:WI232-Jumper-1.JPG}} Lötjumper für Anschluss des Wi232 an den PC (über das MK-USB). <<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:WI232-Jumper-2.JPG}} Lötjumper für Anschluss des Wi232 an den Kopter. <<BR>> <<BR>> = Konfiguration = Nun installiert man das Setup-Tool '''[[attachment:WI232_setup.exe]] '''. Bevor das Programm gestartet wird, sollte das Wi232 in den Programmiermodus versetzt werden. Hierzu wird S3 am Wi232 gebrückt. Am MK-USB den Jumper für die 5V Versorgung aufstecken. Nun das Wi232 an das MK-USB stecken. Jetzt kann die Software gestartet werden. Hier wird die richtige Schnittstelle ausgewählt und die Baudrate auf 2400 gestellt. {{attachment:WI232_SetupTool_Start.JPG}} <<BR>> <<BR>> Die Einstellungen werden wie in den roten Kreisen gezeigt, eingestellt<<BR>> /!\ "Network Mode Register" bei Wi.232 für '''MK''' auf '''"Slave"''', und für die '''PC Seite''' auf '''"Normal"'''. Die Werte können eingestellt und jeweils mit dem "Write" Button gespeichert werden.<<BR>> Nachdem alle Werte gespeichert wurden, wird der Jumper am Wi232 wieder entfernt. Danach kann das Programm geschlossen werden.<<BR>><<BR>> {{attachment:WI232_Setting.JPG}} Hier auf der Abbildung sieht man auch zusätzlich (unten in der Mitte) die drei Statusanzeigen für CTS TXD und RXD. Dabei erkennt man sehr gut, ob man beim Einsatz der SerCon die CTS mit der RTS-Leitung verbunden hat und überhaupt eine Verbindung zustande kommen kann (helles grünes aufleuchten der CTS-Statusanzeige). Zur Sicherheit kann man wie oben gezeigt anschließend den Read-Button drücken, um das Setzen zu verifizieren (für weitere Details siehe [[attachment:Datenblatt.pdf]] ).<<BR>><<BR>> Nach dem schreiben der Werte sollte man '''unbedingt den Jumper von S3 entfernen''', da sonst beim nächsten !PowerUp alle Register auf die Default Settings zurückgesetzt werden.<<BR>><<BR>> '''Schnellanleitung Einstellungen programmieren:''' 1. Jumper auf MK-USB und Wi.232 stecken 1. Wi.232 an den MK-USB anschließen 1. MK-USB an den PC anschließen 1. Radiotronix Software starten (Baudrate auf 2400) und Modul programmieren 1. Jumper auf Wi.232 entfernen 1. Radiotronix Soft schließen 1. MK-USB vom PC trennen 1. Wi.232 vom MK-USB trennen '''Schnellanleitung Einstellungen abrufen (überprüfen):''' 1. Jumper auf MK-USB stecken 1. Wi.232 an den MK-USB anschließen 1. MK-USB an den PC anschließen 1. '''Jetzt erst den Jumper auf das Wi.232 stecken!''' 1. Radiotronix Software starten (Baudrate jetzt auf 57600!) 1. Einstellungen des Moduls prüfen 1. Jumper auf Wi.232 entfernen 1. Radiotronix Soft schließen 1. MK-USB vom PC trennen 1. Wi.232 vom MK-USB trennen Der wichtige Punkt ist: Den Jumper des Wi.232 erst stecken nachdem es Strom hat! So geht das Modul in den Kommando-Modus. ''Die Parameter werden aber nicht gelöscht.'' |
/!\ Because the modules are sensitive to electrostatic they should be used only shrunk. In addition avoid the direct touch of the antenna! = Start up = To configure the module you need first a serial connection with 5V-level to a Windows PC. The easiest way is it to use the MK-USB. Alternatively you can also use the SerCon (connected to SIO). The 5V supply must be extra created when using the SerCon.<<BR>> Using the SerCon it '''must be ''' necessarely be connected for communication with the CTS and RTS-Line of the Sub-D-socket of the Sercon. This is necessary so the level of the CTS line is high. Only in this way a connection with the tool Radiotronix can be set up (Sub-D-socket, connect Pin 7 and 8 at the Standard 9pol. RS 232). You can also have a small toggle switch directly soldered to the pins, and so those have on-demand connection.<<BR>><<BR>> To connect the PC to the copter two identical Wi232 modules are required.<<BR>> To program the modules the jumpers S1 and S2 for TxD / RxD have to be soldered as follows:<<BR>><<BR>> {{http://mikrokopter.de/ucwiki/RadioTronix?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=WI232-Jumper-1.JPG}} Jumper for programming <<BR>><<BR>> /!\ '''N O T E''': the Wi232 module on the PC (connected via the USB MK) and the module on the Kopter are jumpered differently '''after''' programming for TxD / RxD over the jumper S1/S2:<<BR>><<BR>> {{http://mikrokopter.de/ucwiki/RadioTronix?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=WI232-Jumper-1.JPG}} Jumpers for connecting the Wi232 to the PC (via USB MK). <<BR>><<BR>> {{http://mikrokopter.de/ucwiki/RadioTronix?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=WI232-Jumper-2.JPG}} Jumpers for connecting the Wi232 to the Kopter. <<BR>> <<BR>> = Configuration = Now install the Setup Tool: '''[[http://mikrokopter.de/ucwiki/RadioTronix?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=WI232_setup.exe|Download]] '''. Before the program starts the Wi232 should be set into programming mode. For this purpose, S3 is bridged at Wi232. On MK-USB attach the jumper for the 5V supply. Now plug the Wi232 to the MK-USB. The software can be started. Here is the correct interface selected and sets the baud rate to 2400. {{http://mikrokopter.de/ucwiki/RadioTronix?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=WI232_SetupTool_Start.JPG}} <<BR>> <<BR>> The settings are set as shown in the red circles <<BR>> /!\ "Network Mode Register" at the Wi.232 for '''MK''' to '''"Slave"''', and for the '''PC Side''' to '''"Normal"'''. The values can be stored in each set with the "Write" button.<<BR>> After all values have been stored, the jumper can be removed on Wi232. After that the program can be closed.<<BR>><<BR>> {{http://mikrokopter.de/ucwiki/RadioTronix?action=AttachFile&do=get&target=WI232_Setting.JPG}} Click on the picture you can see in addition (bottom center), the three status indicators for TXD,RXD and CTS. It can be seen very well if for the use of the SerCon the CTS and RTS-Lines are connected so that can be established a connection (bride green glow of the CTS-status display). For safety, you can as shown above press the read button to verify the setting (for more details see [[attachment:Datenblatt.pdf]] ).<<BR>><<BR>> After writing the values you should '''necessarily remove the jumper from S3''', otherwise the next time !PowerUp resets all registers to their default settings.<<BR>><<BR>> '''Quick Guide: Program Settings:''' 1. Place Jumper on MK-USB and Wi.232 1. Connect Wi.232 to the MK-USB 1. Connect MK-USB to the PC 1. Start Radiotronix Software (Baud rate to 2400) and program modul 1. Remove Jumper from Wi.232 1. Close Radiotronix Soft 1. Disconnect MK-USB from PC 1. Disconnect Wi.232 from MK-USB '''Quick Guide: Get Settings (to check):''' 1. Place Jumper on MK-USB 1. Connect Wi.232 to the MK-USB 1. Connect MK-USB to the PC 1. '''Now place the jumper on the Wi.232 !''' 1. Start Radiotronix Software (Baud rate now to 57600!) 1. Check settings of the modul 1. Remove jumper from Wi.232 1. Close Radiotronix Software 1. Disconnect MK-USB from PC 1. Disconnect Wi.232 from MK-USB The important point is: Place the jumper of the Wi.232 after power is supplied! So the modul is turning into the Command-Mode. ''The parameters are not deleted.'' |
| Zeile 208: | Zeile 207: |
| Alternativ kann man anstatt das Original-Tools auch das Tool von StompSC vom Arm-O-Kopter-Forum benutzen.<<BR>> Downloadlink: [[http://www.armokopter.at/forum/download/file.php?id=1221|StompSC]]<<BR>> Forumbeitrag: [[http://www.armokopter.at/forum/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=314|Link]]<<BR>><<BR>> = Tip! = Sind die Tx und Rx Lötjumper schon für den Anschluß am MK und am MK-USB gesetzt und das Modul eingeschrumpft, so ist es nicht mehr möglich das MK Modul am MK-USB zu betreiben, zB. um es neu zu programmieren. Die Lösung: Man lötet sich einen 10 poligen Stiftleisten / Buchsenleisten Adapter bei dem die Tx und Rx Leitung gekreuzt werden, Masse und +5 V werden eins zu eins durchgeschleift. Damit kann man das Modul f. den MK wieder am MK-USB anschließen ohne den Schrumpfschlauch zu entfernen und ohne die Tx Rx Jumper umlöten zu müssen. |
= TIP! = Are the jumper for Tx and Rx already set for connection of the MK and the MK-USB and the module is shrunk so it is no longer possible for the MK to operate the MK-USB module, for example to re-program it. The solution: You should solder a 10 pin male connector / socket connector - adapter where the Tx and Rx line been crossed, ground and +5 V can be looped through one to one. Thus you can connect the module back from the MK to the MK-USB without removing the heat shrink stubing and without soldering the Tx / Rx jumpers back. |
| Zeile 222: | Zeile 219: |
| = Anschluss an SerCon / MK-USB = siehe oben, Hinweis auf 5V Versorgung = Anschluss an FC = |
= Connection to SerCon / MK-USB = see above, Note to 5V Supply = Connection to FC = |
| Zeile 228: | Zeile 225: |
| Pin 1 ist mit dem roten Pfeil markiert. Die Spannungsversorgung des Wi232 erfolgt über die FC. = Anschluss an NC = |
Pin 1 is marked with the red arrow. The power supply of the Wi232 via the FC. = Connection to NC = |
| Zeile 236: | Zeile 233: |
| Pin 1 ist mit dem roten Pfeil markiert. Die Spannungsversorgung des Wi232 erfolgt über die Navi.<<BR>> Beim Anschluss an NC (freie 10 pol.Stiftleiste Debugport) sieht man im Koptertool alle angeschlossenen Module (FC,NC,Mk3MAG,GPS) |
Pin 1 is marked with a red arrow. The power supply of the Wi232 via the Navi.<<BR>> When connected to the NC (open 10-pin debug port, pin header) all connected modules can be seen in the Koptertool (FC, NC, MK3Mag, GPS) |
| Zeile 239: | Zeile 236: |
| /!\ Das SW-Update der NC mit den WI232 Modulen ist äußerst problematisch, denn der Upload Prozess endet meist mit einem Fehler. Offensichtlich verträgt sich das serielle Protokoll-Timing des Bootloaders nicht mit dem WI232. Daher sollte man bei einem SW-Update der NC immer direkt ein Kabel anstecken. Das SW-Update des MK3MAG und der FC funktioniert hingegen problemelos. = Rangeextender für PC oder Handy (DubWise) = |
/!\ The SW update of the NC with the WI232 modul is extremely problematic, because the upload process usually ends with an error. Obviously the serial protocol is compatible but the timing of the boot loader does not match the WI232. Therefore you should always hook up directly a cable to the NC for a software update. The software update of the MK3Mag and the FC is, however, unproblematical. Anhören Umschrift Übersetzung bewerten = Rangeextender for PC or Cell (DubWise) = |
| Zeile 244: | Zeile 245: |
| (hier am Beispiel mit der YagiAntenne) Um von Bluetooth auf Wi232 umzusetzen, muss lediglich eine weitere Buchsenleiste auf das Kabel aufgekrimt werden, wo das [[http://www.mikrokopter.de/ucwiki/F2M03GXA|Bluetoothmodul]] (im Slave-Mode) angeschlossen wird. Beide Module müssen dann lediglich mit Spannung (4,5-12V) versorgt werden (Plus an Pin 2 und Minus an Pin 7 des Flachbandkabels) = Reichweitentest = Ein Reichweitentest ergab 1300m am Boden bei Sichtverbindung mit dem EUR-R Modul und 8,6cm Drahtantenne und 6km mit einer YagiAntenne = Yagiantenne für grössere Reichweiten = Eine UHF-Fernsehantenne wie z.B. die [[http://www.reichelt.de/?;ACTION=3;LA=4;GROUP=FA2;GROUPID=3546;ARTICLE=51317|UHF43]] von Reichelt, erhöht die Reichweite erheblich. Damit haben wir schon Positionsdaten des MikroKopters aus 6km Entfernung empfangen. Die Antenne kann gekürzt werden, indem das vordere Element nicht montiert wird (wie auf den Bildern). Dadurch verringert sich etwas die Reichweite, aber die Antenne ist leichter handzuhaben und die Richtwirkung ist nicht mehr so hoch. |
(here in example with a Yagi-Antenna) To implement Bluetooth on Wi232 there must be just another female connector crimped onto the cable, where the [[http://www.mikrokopter.de/ucwiki/F2M03GXA|Bluetoothmodul]] is connected (slave mode). Both modules just only need to be supplied with voltage (4.5-12V) (plus and minus to Pin 2 to Pin 7 of the ribbon cable) = Range Test = A range test was 1300m on the ground in the line of sight, with the EUR-R Modul and 8.6 cm wire antenna. 6km with a Yagi-Antenna. = Yagi-antenna for greater distance = A UHF television antenna e.g. the [[http://www.reichelt.de/; ACTION = 3; LA = 4; GROUP = FA2; GROUPID = 3546;? ARTICLE = 51 317 | UHF43]]of Reichelt, increases the range. We have already received position datas from the MikroKopter 6km away. The antenna can be shortened by the front element if that is not mounted (as in pictures). This will reduce the range somewhat, but the antenna is easier to handle and the straightening effect is not as high. |
| Zeile 260: | Zeile 261: |
| Dazu kann das Wi232 mit Adapter direkt in den Anschlusskasten der Antenne eingebaut werden. Die BNC-Anschlussbuchse wird dazu ausgelötet. Der Antennenanschluss wird an den mittleren Pin angelötet. | Therefore the Wi232 with adapter can be built in directly into the terminal box of the antenna. The antenna connector is soldered to the middle pin. The BNC-Connector is soldered off. |
| Zeile 264: | Zeile 265: |
| = Probleme = Es gibt scheinbar Probleme mit HF-Einstrahlung am Gier-Gyro. Muss noch weiter erforscht werden: http://forum.mikrokopter.de/topic-post113611.html |
= Problems = There are probably problems with the radiation to the gyros. It must be still investigated. http://forum.mikrokopter.de/topic-post113611.html |
|
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- Wi.232 Moduls
- Download Configuration Tool
- Adapter Board
- Layout / wiring diagram
- Placement
- BOM (Bill of Material)
- Assembly
- Ribbon cable
- Start up
- Configuration
- TIP!
- Note:
- Connection to SerCon / MK-USB
- Connection to FC
- Connection to NC
- Rangeextender for PC or Cell (DubWise)
- Range Test
- Yagi-antenna for greater distance
- Problems
Wi.232 Moduls
Shoplink Wi.232 Funkmodul+Adapterplatine
Shoplink Wi.232 Funkmodul
The Wi.232 modules of Radiotronix are a family of wireless modems for wireless bridging and designed especially for serial UARTs. Inside of this family there are several pin-compatible module versions:
Modul description |
Frequency range |
Transmitting Power |
Modulation |
Description |
Wi.232DTS-R |
902 - 928 MHz |
25 mW |
FSK/DTS |
Embedded Radio Module with MCU, Transparent UART to RF Digital Transmission System (DTS) SW protocol (North America) |
Wi.232FHSS-25-R |
902 - 928 MHz |
25 mW |
FHSS/FSK |
Embedded Radio Module with MCU, 25mW, Transparent UART to RF Frequency Hopping Spread Spectrum (FHSS) Protocol (North America) |
Wi.232DTSB-R |
902 - 907.5 & 915 - 928 MHz |
25 mW |
FSK/DTS |
Embedded Radio Module with MCU, Transparent UART to RF Digital Transmission System (DTS) SW protocol, Anatel Certified (Brazil) |
Wi.232EUR-R |
868 - 870 MHz |
32 mW |
FSK/DTS |
Embedded Radio Module with MCU, Transparent UART to RF Digital Transmission System (DTS) SW protocol, ETSI Regulations Compliant (Europe) |
All modules require a power supply of 2.7 - 3.6 volts at a current of max. 65 mA and support baud rates from 2400 up to 115,200. On this Paparazzi page you will be discouraged from using the North America version, since they may interfere with GPS reception.
The modules you can get here:MK-Shop
Download Configuration Tool
Adapter Board
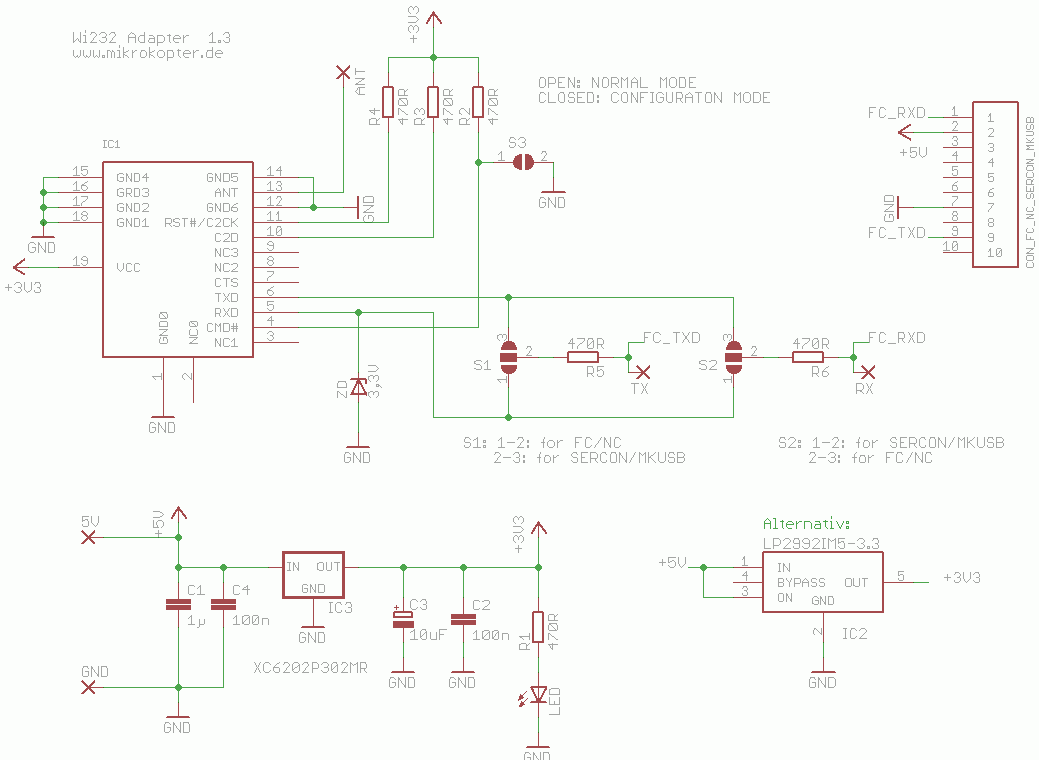
![]() The adapter board is suitable for the MikroKopter as well as for the PC side! On the PC side the module is connected to the MK-USB. To use these modules in addition to a suitable antenna (a 8.6 cm long isolated wire) you may need an adapter board, which handles the voltage supply and the level shifter from 5V TTL to 3.3V or 3V TTL. The adapter board was developed following the recommendation of the Modul-Datenblattes and the Bluetooth Adapter BT-AP10.
The adapter board is suitable for the MikroKopter as well as for the PC side! On the PC side the module is connected to the MK-USB. To use these modules in addition to a suitable antenna (a 8.6 cm long isolated wire) you may need an adapter board, which handles the voltage supply and the level shifter from 5V TTL to 3.3V or 3V TTL. The adapter board was developed following the recommendation of the Modul-Datenblattes and the Bluetooth Adapter BT-AP10.
There are two versions of the adapter board which differ only slightly.
Old Version
Version V1.3

Layout / wiring diagram
Old Version
Version V1.3
Placement
Old Version
Version V1.3
BOM (Bill of Material)
Old Version |
Name |
Number |
Description |
Ordering Number |
Note |
IC1 |
1 |
WI.232EUR-R |
MK-Shop or Sander Electronics |
All Versions |
IC2 |
1 |
LP2992IM5-3.3 |
CSD Elektronics 22-2992V03,3 |
Voltage Converter 3,3V |
C1 |
1 |
0805 KerKo 1 µF / 16V |
CSD Elektronics 115-08R001 |
|
C2 |
1 |
0805 KerKo 100 nF |
CSD Elektronics 115-08N100 |
|
C3 |
1 |
T4.7µF / 10V |
CSD Elektronics 121-A10R004,7 |
Watch Polarity !! |
R1 |
1 |
0805 SMD 330 Ohm |
CSD Elektronics 10-080330 |
|
R2, R3, R4, R5, R6 |
5 |
0805 SMD 1k Ohm |
CSD Elektronics 10-08K001 |
|
LED |
1 |
LED 0805 GRN |
CSD Elektronics 26-0802017 |
All Versions, Watch Polarity |
ZD |
1 |
Z-Diode SMD 3,3V |
CSD Elektronics 13203 |
All Versions, Watch Polarity ! |
S3 |
1 |
Pin-header 2-pole RM 2.54 mm |
CSD Elektronics 01541 |
All Versions, only for programming the modules |
Ribbon cable |
1 |
10 Pol, RM 1.27mm |
CSD Elektronics 456-10 |
Pin 1 (red wire shows to R6) |
Header Connector |
1 |
10 Pole, IDC socket |
CSD Elektronics 015-PF10 |
|
Antenna |
1 |
8.6 cm wire stub |
- |
Lamda/4 of 870MHz |
V1.3 |
Name |
Number |
Description |
Ordering Number |
Note |
IC1 |
1 |
WI.232EUR-R |
MK-Shop or Sander Electronics |
All Versions |
IC3 |
1 |
XC6202P302MR |
??? |
alternativ to IC2 (3V) |
C1 |
1 |
0805 KerKo 1 µF / 16V |
CSD Elektronics 115-08R001 |
|
C2, C4 |
2 |
0805 KerKo 100 nF |
CSD Elektronics 115-08N100 |
|
C3 |
1 |
T10 µF / 10V |
121-A10R010 |
Watch Polarity (Currently one KerKo is supplied by the MK-Shop, here you don't have to watch the polarity!) |
R1, R2, R3, R4, R5, R6 |
6 |
0805 SMD 470 Ohm |
CSD Elektronics 10-080470 |
|
LED |
1 |
LED 0805 GRN |
CSD Elektronics 26-0802017 |
All Versions, Watch Polarity! |
ZD |
1 |
Z-Diode SMD 3,3V |
CSD Elektronics 13203 |
All Versions, Watch Polarity! |
S3 |
1 |
Pin header 2-pole RM 2.54 mm |
CSD Elektronics 01541 |
All Versions, only for the programming of the modules |
Ribbon cable |
1 |
10 ole, RM 1.27mm |
CSD Elektronics 456-10 |
Pin 1 (red wire points to R6) |
Header Connector |
1 |
10 pole, IDC socket |
CSD Elektronics 015-PF10 |
|
Antenna |
1 |
8.6 cm wire stub |
- |
Lamda/4 of 870MHz |
In the MK-Shop you can get a set with all components.
Assembly
First you need to solder the resistors R1 to R6, the IC3 (IC2 remains unpopulated here), the diodes D1, D2 and capacitors C1 to C4 at the bottom of the board.
Then you need to assemble the jumper S3 and possibly the 10-pin ribbon cable with Pin1 (red side) down to R6.
Now you check for shorts and put 5V on a trial basis between the 5V and GND pad.
The green LED should light and between the GND pad and the pad of the separately module located between R6 and C1 there should be 3.3V or 3V (at XC6202P302MR) applied.
![]() Attention! Only after the test was successful you solder the Wi.232 module on the other side of the board and check the pads of the module for short circuits (very narrow pitch, threat of destruction of the Wi.232 module!). Only the four-row should have a short circuit between all four pins, otherwise not be measured between adjacent pins.
Attention! Only after the test was successful you solder the Wi.232 module on the other side of the board and check the pads of the module for short circuits (very narrow pitch, threat of destruction of the Wi.232 module!). Only the four-row should have a short circuit between all four pins, otherwise not be measured between adjacent pins.
At the end the wire stub can be added to the pad of the antenna.
The result looks like this:
![]() In the old layout unfortunately an error crept in so that GND is tapped at pin 7 of the 10-pin ribbon cable to the board at pin 8. This explains the small patch in the upper right picture. On the ribbon cable pin 8 is "unproductive" and bridged on the PCB with pin 7 & 8
In the old layout unfortunately an error crept in so that GND is tapped at pin 7 of the 10-pin ribbon cable to the board at pin 8. This explains the small patch in the upper right picture. On the ribbon cable pin 8 is "unproductive" and bridged on the PCB with pin 7 & 8
Is resolved in V1.3 !
Ribbon cable
The ribbon cable should be about 9cm long. The transmitter then has some distance to the remaining electronic. In addition the ribbon cable is then the opposite pole of the antenna.
![]() Because the modules are sensitive to electrostatic they should be used only shrunk. In addition avoid the direct touch of the antenna!
Because the modules are sensitive to electrostatic they should be used only shrunk. In addition avoid the direct touch of the antenna!
Start up
To configure the module you need first a serial connection with 5V-level to a Windows PC.
The easiest way is it to use the MK-USB. Alternatively you can also use the SerCon (connected to SIO). The 5V supply must be extra created when using the SerCon.
Using the SerCon it must be necessarely be connected for communication with the CTS and RTS-Line of the Sub-D-socket of the Sercon. This is necessary so the level of the CTS line is high. Only in this way a connection with the tool Radiotronix can be set up (Sub-D-socket, connect Pin 7 and 8 at the Standard 9pol. RS 232). You can also have a small toggle switch directly soldered to the pins, and so those have on-demand connection.
To connect the PC to the copter two identical Wi232 modules are required.
To program the modules the jumpers S1 and S2 for TxD / RxD have to be soldered as follows:
Jumper for programming
![]() N O T E: the Wi232 module on the PC (connected via the USB MK) and the module on the Kopter are jumpered differently after programming for TxD / RxD over the jumper S1/S2:
N O T E: the Wi232 module on the PC (connected via the USB MK) and the module on the Kopter are jumpered differently after programming for TxD / RxD over the jumper S1/S2:
Jumpers for connecting the Wi232 to the PC (via USB MK).
Jumpers for connecting the Wi232 to the Kopter.
Configuration
Now install the Setup Tool: Download .
Before the program starts the Wi232 should be set into programming mode. For this purpose, S3 is bridged at Wi232. On MK-USB attach the jumper for the 5V supply. Now plug the Wi232 to the MK-USB. The software can be started. Here is the correct interface selected and sets the baud rate to 2400.
The settings are set as shown in the red circles
![]() "Network Mode Register" at the Wi.232 for MK to "Slave", and for the PC Side to "Normal".
"Network Mode Register" at the Wi.232 for MK to "Slave", and for the PC Side to "Normal".
The values can be stored in each set with the "Write" button.
After all values have been stored, the jumper can be removed on Wi232. After that the program can be closed.
Click on the picture you can see in addition (bottom center), the three status indicators for TXD,RXD and CTS. It can be seen very well if for the use of the SerCon the CTS and RTS-Lines are connected so that can be established a connection (bride green glow of the CTS-status display). For safety, you can as shown above press the read button to verify the setting (for more details see Datenblatt.pdf ).
After writing the values you should necessarily remove the jumper from S3, otherwise the next time PowerUp resets all registers to their default settings.
Quick Guide: Program Settings:
- Place Jumper on MK-USB and Wi.232
- Connect Wi.232 to the MK-USB
- Connect MK-USB to the PC
- Start Radiotronix Software (Baud rate to 2400) and program modul
- Remove Jumper from Wi.232
- Close Radiotronix Soft
- Disconnect MK-USB from PC
- Disconnect Wi.232 from MK-USB
Quick Guide: Get Settings (to check):
- Place Jumper on MK-USB
- Connect Wi.232 to the MK-USB
- Connect MK-USB to the PC
Now place the jumper on the Wi.232 !
- Start Radiotronix Software (Baud rate now to 57600!)
- Check settings of the modul
- Remove jumper from Wi.232
- Close Radiotronix Software
- Disconnect MK-USB from PC
- Disconnect Wi.232 from MK-USB
The important point is: Place the jumper of the Wi.232 after power is supplied! So the modul is turning into the Command-Mode. The parameters are not deleted.
(tbd. Register für MTU & Tx-Timeout auf serielles Protokoll / FW-Update optimieren)
TIP!
Are the jumper for Tx and Rx already set for connection of the MK and the MK-USB and the module is shrunk so it is no longer possible for the MK to operate the MK-USB module, for example to re-program it.
The solution: You should solder a 10 pin male connector / socket connector - adapter where the Tx and Rx line been crossed, ground and +5 V can be looped through one to one.
Thus you can connect the module back from the MK to the MK-USB without removing the heat shrink stubing and without soldering the Tx / Rx jumpers back.
Note:
- There is a slight difference in setting up the module for the MK and the one for the USB link. The one connected to the USB link will have to be set up as "Normal" under the "Network Mode Register" and the one connected to the MK will have to be set to "Slave" for the Wi.232 link to work properly.
Connection to SerCon / MK-USB
see above, Note to 5V Supply
Connection to FC
Pin 1 is marked with the red arrow. The power supply of the Wi232 via the FC.
Connection to NC
Pin 1 is marked with a red arrow. The power supply of the Wi232 via the Navi.
When connected to the NC (open 10-pin debug port, pin header) all connected modules can be seen in the Koptertool (FC, NC, MK3Mag, GPS)
![]() The SW update of the NC with the WI232 modul is extremely problematic, because the upload process usually ends with an error. Obviously the serial protocol is compatible but the timing of the boot loader does not match the WI232. Therefore you should always hook up directly a cable to the NC for a software update. The software update of the MK3Mag and the FC is, however, unproblematical. Anhören Umschrift Übersetzung bewerten
The SW update of the NC with the WI232 modul is extremely problematic, because the upload process usually ends with an error. Obviously the serial protocol is compatible but the timing of the boot loader does not match the WI232. Therefore you should always hook up directly a cable to the NC for a software update. The software update of the MK3Mag and the FC is, however, unproblematical. Anhören Umschrift Übersetzung bewerten
Rangeextender for PC or Cell (DubWise)
(here in example with a Yagi-Antenna)
To implement Bluetooth on Wi232 there must be just another female connector crimped onto the cable, where the Bluetoothmodul is connected (slave mode). Both modules just only need to be supplied with voltage (4.5-12V) (plus and minus to Pin 2 to Pin 7 of the ribbon cable)
Range Test
A range test was 1300m on the ground in the line of sight, with the EUR-R Modul and 8.6 cm wire antenna. 6km with a Yagi-Antenna.
Yagi-antenna for greater distance
A UHF television antenna e.g. the UHF43of Reichelt, increases the range.
We have already received position datas from the MikroKopter 6km away.
The antenna can be shortened by the front element if that is not mounted (as in pictures). This will reduce the range somewhat, but the antenna is easier to handle and the straightening effect is not as high.
Therefore the Wi232 with adapter can be built in directly into the terminal box of the antenna. The antenna connector is soldered to the middle pin. The BNC-Connector is soldered off.
Problems
There are probably problems with the radiation to the gyros. It must be still investigated. http://forum.mikrokopter.de/topic-post113611.html
RadioTronix/../ucwiki/KategorieHardware

 Seite in
Seite in